If translating XML files online (Extensible Markup Language File Format) is an important part of your organization’s data localization process, it’s no wonder you want to learn the best way to translate XML files and get an online XML translator recommendation.
An XML file, in the words of Harvard Business Review, is “a more flexible cousin of HTML.” In other words, XML files allow custom tags, code and other labels that describe the data in the file.
Due to this custom markup, XML file translation isn’t as simple and straightforward as Word document translation.
To make it easier and faster to translate an XML file online into another language, use enterprise translation software optimized for XML files. This applies whether you translate XLIFF files, databases or data feeds.
Read this list of the top features to look for in an XML translator online. We’ll recommend an efficient solution at the end of this post that avoids breaking code and wasting tokens.
Quick XML translator recommendation
If you want the fastest and safest way to translate XML files online, use a translation tool designed specifically for structured data formats — not a general-purpose chatbot or consumer translator.
Even better, if you want to translate XML files online securely, use Pairaphrase. It’s the secure AI Translation Management System built for enterprises, with AI guardrails that keep also your XML tags, structure, attributes, placeholders, and links protected.
Pairaphrase has a built-in XML parser to prevent XML code from breaking during translation, and it doesn’t burn through tokens like many other AI translation tools.
Why take our advice on translating XML files?
As translation industry veterans with decades of first-hand experience supporting software, product, and localization groups, we’ve helped organizations across the world translate structured data safely and at scale.
We work closely with developers, content teams, and enterprise stakeholders, so we’ve seen firsthand where XML files break, how placeholders get lost, and why quick fixes often turn into production issues. Our platform reflects that real-world insight and includes:
-
Agentic AI + Generative AI tuned for structured content
-
(Chat)GPT-powered translation workflows with code-safe guardrails
-
Terminology Management + Translation Memory for brand consistency
-
Secure, encrypted workspace for XML and multilingual content
-
Developer‑friendly workflows for product feeds, PIM systems, apps, and sitemaps
Today, we’ll show you why these features are so important for a smooth XML file translation workflow.
What you’ll learn in this article
Here’s what you’ll learn about how to translate XML files safely and efficiently:
-
How to translate XML files online, step by step
-
Why XML presents unique translation challenges
-
The most important features in a modern XML translation tool
-
How to translate an XML file online without breaking code
-
How to protect tags, attributes, IDs, and links during translation
-
Steps to keep your schema valid before and after translation
Why translating XML files is different (and why it goes wrong)
Here are the pain points most teams face when translating XML files:
-
Tags get translated or rearranged — breaking the file.
-
Attributes or URLs are altered — causing redirects, bad links, or product errors.
-
Nesting is lost or malformed — creating validation failures.
-
AI “creativity” slips into markup — inserting unexpected characters or reformatting code.
-
Internal placeholders or IDs change — causing app or content failures.
These problems aren’t about skill, they’re about using the wrong tool. XML needs a translation workflow that’s structured, protected, and code‑safe.
Preparing XML for translation (before you upload your file)
Before you translate XML files online, a little prep work goes a long way. It reduces the risk of broken code, failed imports, and last‑minute fire drills.
Step‑by‑step XML translation prep checklist
Use this quick checklist before you upload your XML for translation:
-
Validate your XML against its schema (XSD or DTD), ensuring nesting, tag order, and closing tags are correct before translation.
-
Back up the original files in a safe location so you can always roll back.
-
Confirm the encoding (UTF‑8 is usually the safest choice for multilingual XML).
-
Separate user‑visible text from technical content where possible.
-
Mark non‑translatable content such as IDs, codes, variables, and internal comments.
Internationalization and design best practices
Good internationalization (I18N) makes it easier to translate XML files correctly the first time:
-
Avoid putting large amounts of translatable text inside attributes when you can use elements instead.
-
Keep messages complete (avoid splitting sentences across multiple tags).
-
Use placeholders safely (e.g., {0}, %s) and document what they represent.
-
Always use a Unicode‑friendly encoding so you can support every target language.
-
Provide short notes or comments so translators understand context, UI constraints, and character limits.
Quality assurance and common pitfalls
After you translate an XML file, build QA into your workflow:
-
Re‑run schema and well‑formedness checks.
-
Verify placeholder consistency and tag integrity.
-
Spot‑check layout or length issues after the XML is imported back into your app, site, or feed.
Common mistakes to avoid
-
Editing or deleting tags instead of just the text.
-
Changing IDs, internal codes, or file paths.
-
Mixing encodings across files.
-
Translating internal codes or variables.
-
Ignoring pluralization or language‑specific grammar rules.
Code-Safe AI Translation
When you translate XML, your translation tool must protect the technical parts of your file—not interpret them. If you’re using AI-powered XML file translators, remember: a code-safe XML workflow keeps structure intact by safeguarding:
-
URLs and internal links
-
Attributes, IDs, and SKUs
-
Placeholders and variables ({0}, %s, )
-
Escape sequences and structured values
These protections help you translate XML without breaking tags, logic, or links.
How to translate an XML file, step-by-step
To translate XML files safely and quickly, follow these steps using Pairaphrase’s file translator:
1. Create or log in to your Pairaphrase account
Start by purchasing a Pairaphrase plan or logging into your existing account. Pairaphrase is an AI Translation Management System of the highest quality.
2. Upload your XML file (or a batch of files)
Go to the File Translator and upload your .xml file. If you manage multiple locales or environments, you can upload several XML files at once.
If you want more guidance on how to prepare an XML for translation, read below.
3. Choose your target language(s)
Select the language(s) you want to translate into.
Here, you define your XML localization workflow—pilot language or multi-market release.
4. Click “Translate File” to generate your XML draft
Pairaphrase:
-
Parses your XML structure
-
Separates text from tags
-
Protects attributes, placeholders, IDs, and URLs
-
Keeps your formatting and nesting intact
This gives you a clean first draft that’s code-safe.
5. Review and refine in the XML Translation Editor
Open your translated file in the editor to:
-
Adjust tone and terminology
-
Confirm UI/product language accuracy
-
Reuse Translation Memory for repeated segments
Because the editor is XML-aware, you never touch the markup—only the text.
6. Download your translated XML file
From the File Editor, export your final XML. The structure, encoding, tagging, and nesting remain exactly as in the original—ready to be dropped back into your product, feed, or CMS without cleanup.
Over time, your Translation Memory helps you translate XML faster and with lower token usage.
Best Features to Look for in XML Translation Software
1. Sufficient language pairs for XML file translation
When you translate XML files across multiple markets—product feeds, app strings, help content, or sitemaps, you need a translation system with broad language coverage.
XML is used globally, so your tool should support both your current locales and the languages you expect to expand into over time.
A strong XML translator should include 140+ languages, including English, Spanish, German, French, Hindi, Arabic, Japanese, and more.
2. Translates more than XML files
If your organization also translates non-XML files, find XML translator software that also performs file translation for other formats.
Developers, product teams, and localization managers often work with JSON, HTML, XLIFF, CSV, and other formats in the same release cycle. Your XML translator should support all of them so you don’t juggle multiple tools or fragment your Translation Memory.
Pairaphrase File Formats
Microsoft
Word (.docx)
Excel (.xlsx)
PowerPoint (.pptx)
Outlook (.msg)
Google Drive
Google Docs (.gdoc)
Google Sheets (.gsheet)
Google Slides (.gslides)
Adobe
Digital PDF (.pdf)
Scanned PDF (.pdf)
InDesign (.idml)
eLearning
XLIFF 1.2
XLIFF 2.0
Audio & Video
MP3 Audio (.mp3)
MP4 Video (.mp4)
WAV Audio (.wav)
YouTube Subtitles (.srt)
MicroDVD subtitle files (.sub)
WebVTT (.vtt)
Software Development
Resource Files (.strings)
JSON (.json)
Portable Objects (.po)
XML
XML for Android
Other
Email (.eml)
HTML
AutoCAD (.dxf)
Rich Text Format (.rtf)
Plain Text (.txt)
3. AI XML file translator
The best XML translators combine traditional Machine Translation (MT) with Agentic AI Translation and structured-content safeguards. This hybrid approach keeps your XML clean, protects markup, and ensures your first draft is high-quality—not a messy starting point.
Why you typically burn through AI tokens when translating XML
If you’ve tried to use AI to translate XML with tools like ChatGPT, you’ve likely noticed that you unnecessarily burn through tokens. This is because the AI tool is counting the tags, line breaks, and indentations as tokens, in addition to the actual text and punctuation.
Also, because XML often contains repeated labels, product data, and UI strings across hundreds of nodes, a naïve AI translator will re-translate every instance and burn through tokens this way.
How to avoid burning through tokens during XML translation
Using an AI XML translator with parsing and Translation Memory built in, like Pairaphrase, is the way to go. It will parse your XML and reuse your approved language segments automatically as part of your plan without depleting tokens.
This way, you reduce translation costs, avoid token waste and keep language consistent across your XML files.
Reusable translations & terminology
Translation Memory and Terminology Management help keep the language in your XML file consistent across releases, especially when the same product names, UI strings, and labels appear in multiple XML files.
This video explains the difference between a Translation Memories and Term Base glossaries.
Translation agent for XML files
An XML-aware translation agent (an “XML translator GPT”) can help clarify tag usage, explain placeholders, catch inconsistencies, and answer questions about complex nested structures. It acts like an on-demand assistant next to your file.
Key agent capabilities (XML-specific):
-
Understanding of tag hierarchy
-
Highlights non-translatable fields
-
Explains placeholders and variables
-
Assists with tone changes and terminology
-
Identifies suspicious text or untranslated segments

In Pairaphrase, the Translation Agent appears beside the File Editor. You can prompt it to get alternate translations, explanations, synonyms, and answer translation general questions.
Model training
Model training for XML content happens through usage, not just by uploading training documents. As you edit translations and refine segments, the system improves its suggestions over time by leveraging the Translation Memory feature. Additionally, when you upload glossaries, your terminology is faithfully applied to your translations.
Key capabilities:
-
Learns preferred phrasing and brand voice
-
Improves accuracy for repeated XML segments
-
Reduces manual editing for future uploads
AI Sandbox
An AI Sandbox lets you test phrasing, restructure content, rewrite labels, or experiment with XML-related instructions without modifying your actual file. It’s helpful for reviewing tone, rewriting product descriptions, or checking alternative variants of UI text.
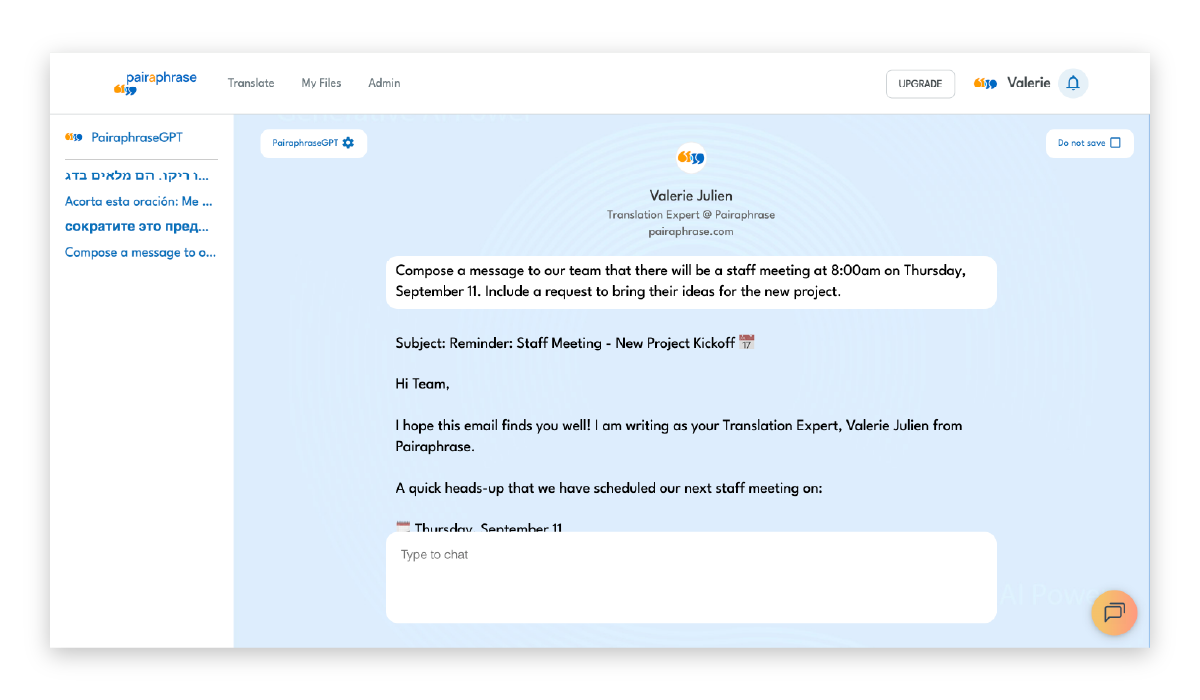
Use Pairaphrase’s AI Sandbox to refine tone, rewrite text, or test variations without modifying your actual XML file.
4. Powerful XML-aware translation editor
A strong XML file translator should include an editing environment that lets reviewers improve machine-translated output while keeping all tags, attributes, and structure protected.
This is essential for XML, where even small markup changes can break your application, feed, or CMS import.
What an XML-aware editor should provide
An effective editor for XML localization should let you:
-
Edit only the text—tags stay locked to prevent structural damage
-
View segments in a clean, readable form without markup clutter
-
Use Translation Memory and Terminology Management to keep phrasing consistent
-
Apply glossary rules and dynamic learning so corrections improve future output
-
Find & replace repeated text instantly, speeding up review across large XML files
-
Reuse approved translations automatically, reducing cost and editing time
These capabilities help teams present high-quality multilingual content with minimal manual cleanup.
Localization QA for XML Files
Even with safeguards, XML translation can introduce subtle issues that only appear during review. Keeping QA close to your editor helps you catch:
-
Missing tags
-
Broken placeholders
-
Truncated text
-
Inconsistent terminology
Spotting these early prevents expensive downstream fixes and ensures your XML re-imports cleanly into your app, site, or system.
5. Multiple translation engines
Different MT engines perform differently depending on language pair and content type. Your XML translator should let you choose from several high-quality engines, including proprietary options like PairaphraseGPT.

Choose from multiple translation engines to get the best results for your XML language pair and content type.
6. Batch XML file translation
Some online XML translation tools only allow translation of XML files one at a time. If you produce large amounts of localized content, this reason alone might be why you want to learn how to translate XML files more productively.
Batch XML file upload matters most for:
-
Product feeds
-
Sitemaps
-
Multilingual app files
-
Multi-locale releases
Your team should be able to upload dozens or hundreds of XML files at once.
XML translators that accept files in batches (groups) are hands down the best way to translate an XML file while saving time. This is also referred to as “batch translation.”
Prevent token waste with batch XML translation
Batch workflows benefit from Translation Memory, which prevents your AI from re-translating identical segments across large XML feeds. This keeps costs down and reduces unnecessary token usage at scale.
7. XML structure & tag preservation
Preserving XML structure is essential when you translate XML files. Even a small change to tags, attributes, or nesting can break your product feed, app strings, or website import.
A strong XML translator should protect your file’s markup while keeping all structural elements intact. Tools like Pairaphrase support XML as a translatable file type and are designed to preserve the original structure as closely as possible.
Structure preservation isn’t perfect for every XML variant—especially highly customized schemas. The XML file translator should reliably keep tags locked, safeguard attributes, and avoid unwanted changes to your markup.
What XML structure preservation should include
A structure-aware XML translation workflow should provide:
-
Locked tags and stable tag order: Preventing AI from rewriting or repositioning XML markup.
-
Protected attributes, IDs, URLs & code elements: Ensuring elements like <title lang="en"> or url="/product/{id}" stay exactly as written.
-
Correct nesting and hierarchy: Avoiding malformed XML or schema errors after translation.
-
Preserved encoding and special characters (UTF-8): Ensuring multilingual text renders properly in your product or CMS.
-
Separation of translatable vs. technical content: Ensuring only the correct text segments are processed.
8. Real-time XML translation collaboration
Does your team collaborate on XML translation? Because of the nature of XML documents and the code within them, it’s likely your localization team will work with your development team.
You need features that help your organization’s departments work together efficiently.
XML workflows often involve developers, product teams, and localization reviewers. Look for collaboration tools such as:
-
Shared access to files and folders
-
Comments & revision history to track decisions
-
Instant messaging for quick clarifications
9. Encrypted cloud storage for XML files
When you translate XML files that contain product data, pricing, or sensitive business content, security and governance are non‑negotiable.
Encrypted cloud storage is an important part of translating XML files online more securely and efficiently. You will eliminate confusion over which file version is the most current while creating centralized access for your authorized colleagues.
XML hosts sensitive data—product info, pricing, customer-facing content. Be sure your XML translator at least includes:
-
Encryption in transit and at rest
-
Role-based access
-
Admin governance
-
Audit trails
10. Robust API for automatic XML workflows
Teams that manage product feeds or application strings often need automated XML translation. An API allows you to:
-
Submit XML for translation when updates occur
-
Connect localization workflows directly to build pipelines
Automation, when set up properly, reduces manual steps and prevents errors.
11. Enterprise security & compliance
Any XML file translator you choose should offer enterprise-grade security. XML files often contain product data, pricing, and user-facing messages—so protecting this content throughout the translation workflow is essential.
If you work in a regulated industry, choose a platform that supports secure file handling and meets compliance requirements such as HIPAA, FERPA, or GDPR. This ensures your translated XML files remain protected end-to-end.
Look for security features such as:
-
multi-factor authentication (MFA)
-
Single Sign-On (SSO)
-
strong encryption
-
regular penetration testing or vulnerability scanning
These safeguards help your team translate XML confidently without putting sensitive data at risk.
12. Compliance support for regulated XML content
If you work in healthcare, finance, education, or government, choose an XML translator that supports compliance frameworks such as HIPAA, FERPA, PCI DSS, GDPR, and SOC 2.
XML files often contain regulated or sensitive information. This could include product identifiers, user-visible messages, help contents, notifications, etc. Therefore, secure handling and compliance becomes especially important during translation.
13. Strict confidentiality for XML files
The XML translation software vendor you choose should not use customer XML files to train public models. This protects sensitive structured content and ensures confidentiality for proprietary code, labels, and identifiers.
14. Fast, responsive human support for XML workflows
When dealing with nested tags, broken placeholders, or import issues, quick human support can prevent a delayed release. Look for same-day responses and knowledgeable technical support staff.
Best way to translate XML files by scenario (comparison table)
Use this table to match your XML translation approach to the scenario you’re dealing with.
|
Scenario |
Recommended approach |
Key safeguards |
How Pairaphrase helps |
|
Small one‑off XML file |
XML editor or text editor + manual translation, or a one‑off upload to an XML‑aware translator |
Back up the original, validate after editing, run a diff check |
Use Pairaphrase’s File Translator for a quick AI + TM‑assisted translation, then download and validate the XML in your editor before deployment. |
|
App or website strings |
XML‑aware CAT/TMS with filters and tag protection |
Protect tags, define translatable fields, add context notes for translators |
Pairaphrase keeps tags intact, lets you lock non‑translatable fields, and reuses TM + terminology across releases so your UI language stays consistent. |
|
Large automated feeds |
Scripted MT + TMS with batch XML upload, TM leverage, and QA checks |
Schema validation, placeholder checks, automated tests in your application |
Pairaphrase handles batch XML translation with TM and QA‑friendly output, while your deployment pipeline runs schema validation and integration tests. |
FAQ
How do I translate XML without breaking code?
To translate XML without breaking code, use an XML‑aware translator that protects tags, attributes, URLs, and placeholders, and then validate the translated file against its schema before deployment.
How do I translate XML without AI burning through tokens?
To translate XML without AI burning through tokens, use a Translation Management System that parses XML, supports large files, uses Translation Memory, and doesn’t tokenize XML tags. Pairaphrase allows you to translate without AI burning through tokens.
Can AI translate XML files safely?
AI can translate XML files safely when you use a platform with Agentic AI guardrails that keep markup locked and prevent the model from rewriting tags or attributes.
What’s the best way to translate XML with tags preserved?
The best way to translate XML with tags preserved is to use a platform that separates text from markup, locks tags automatically, and lets you clearly define which fields are translatable.
Is there a secure way to translate XML files?
The most secure way to translate XML files is to use an enterprise translation platform that provides encryption in transit and at rest, role‑based access controls, and clear governance.
Pairaphrase, for example, keeps XML in an encrypted, permission‑based workspace so enterprise teams can translate safely and with compliance.
Recommended XML file translator
Want to get started with the best XML file translator? Try Pairaphrase. It’s the AI Translation Management System for teams that value smarter, faster, and safer translation.

Pairaphrase supports 140+ languages and 20,000+ language pairs. Translate XML files into Spanish, English, French, German, Arabic, Hindi, Chinese, Japanese, and more. Not to mention, Pairaphrase performs file translation for 25+ file types.
Just one translation with Pairaphrase can cover your annual subscription!
Get Started
Schedule a demo or share this article with a colleague.
“Pairaphrase has enabled us to collaborate with our distribution partners and international sales people to provide correct, quality translations while protecting two of our most valuable resources: time and money.”
- Louis Amos, European Marketing Manager @ The Aquatrols Company



.png)

.png)



